The term GRC – “Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance” gained prominence in the early 21st century when there was an increase in government regulations in various industries to protect consumers, investors, and the environment such as finance and healthcare. Major regulatory changes, such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) in the United States (2002) and the Basel II accord in the banking industry imposed strict governance and compliance requirements on organizations. Another notable example is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in healthcare and the USA PATRIOT Act in the banking sector.
Over time, organizations began to recognize the need for a systematic and holistic approach to governance, risk management, and compliance to ensure effective and efficient operations. The interconnected nature of these functions made it clear that siloed approaches were inadequate.
Today, GRC is an integral part of many organizations’ strategies and operations to ensure that companies are compliant with regulations, manage risks effectively, and maintain ethical governance practices. This involves the use of various tools, methodologies, and technologies that help organizations achieve their strategic and business goals while minimizing potential threats and vulnerabilities.
What is GRC? GRC is a framework or approach used by organizations to manage and align activities relating to governance, risk management, and compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and standards. The framework encompasses a set of practices, policies, processes, and procedures that help organizations achieve their objectives while avoiding legal and regulatory consequences, data breaches and loss, operational disruption and reputational damages.
The GRC frameworks have evolved to encompass a broader range of concerns, including data privacy, cybersecurity, environmental and social responsibilities, ethics, and sustainability. As the business environment becomes more complex due to increases in regulations, advancement of technology, and digital transformation, GRC frameworks are constantly updated to meet the new challenges, for example, the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for agile GRC practices.
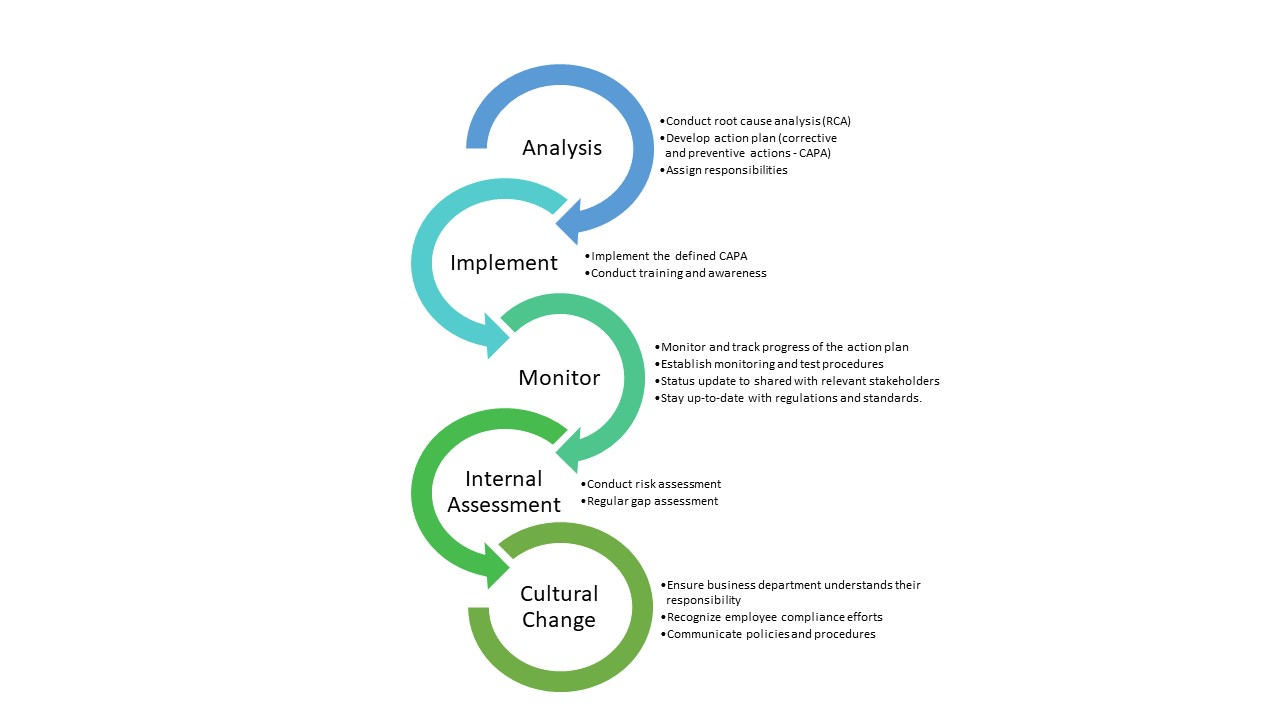
The GRC Functions
Governance: The means by which an organization is directed and controlled is known as governance. In GRC, governance refers to the overall structure and framework of an organization, including its policies, procedures, and decision-making processes. Governance is necessary for setting direction through strategies and policies, monitoring performance and controls, and evaluating outcomes. GRC focuses on establishing and maintaining effective governance practices to ensure that organizations’ objectives align with its mission and values.
Risk Management: Literally, risk refers to a possible event that could cause harm or loss or make it more difficult to achieve objectives. In GRC, risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could impact the organization’s ability to achieve its strategic objectives and goals. GRC helps organizations implement risk management processes to proactively address potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Compliance: This involves adherence to laws, regulations, industry standards, and internal policies that apply to an organization’s operations. GRC assists organizations in taking measures and implementing controls to ensure that compliance requirements are consistently met, thereby preventing legal issues, penalties, and reputational damage.



Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.