Identity Management
In today’s digital era, robust identity management has become a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity strategies, especially with the myriads of regulations aimed at protecting personal data. Effective identity management not only safeguards data but also enhances operational efficiency and trust. Achieving compliance with identity management requires a combination of comprehensive policies, robust technology, and ongoing monitoring. This article delves into strategies for achieving compliance with identity management.
In this context of identity management, “identity” refers to user identifiers and passwords within a system. Identity management systems are used by organizations to manage user identifiers as well as provide a way to manage user access over their lifecycle of roles.
While discussing the strategy for compliance, let us cover the attributes of identity management. Identity management encompasses a range of attributes that collectively ensure secure and efficient management of user identities. Key attributes include:
Authentication: Verifying the identity of users through various methods such as passwords, biometrics verification, or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Authorization: Determining user permissions and access levels to resources based on their verified identity.
User Provisioning and De-provisioning: Managing the creation, updating, and deletion of user accounts and access rights.
Role Management: Defining and managing roles and associated permissions to streamline access control.
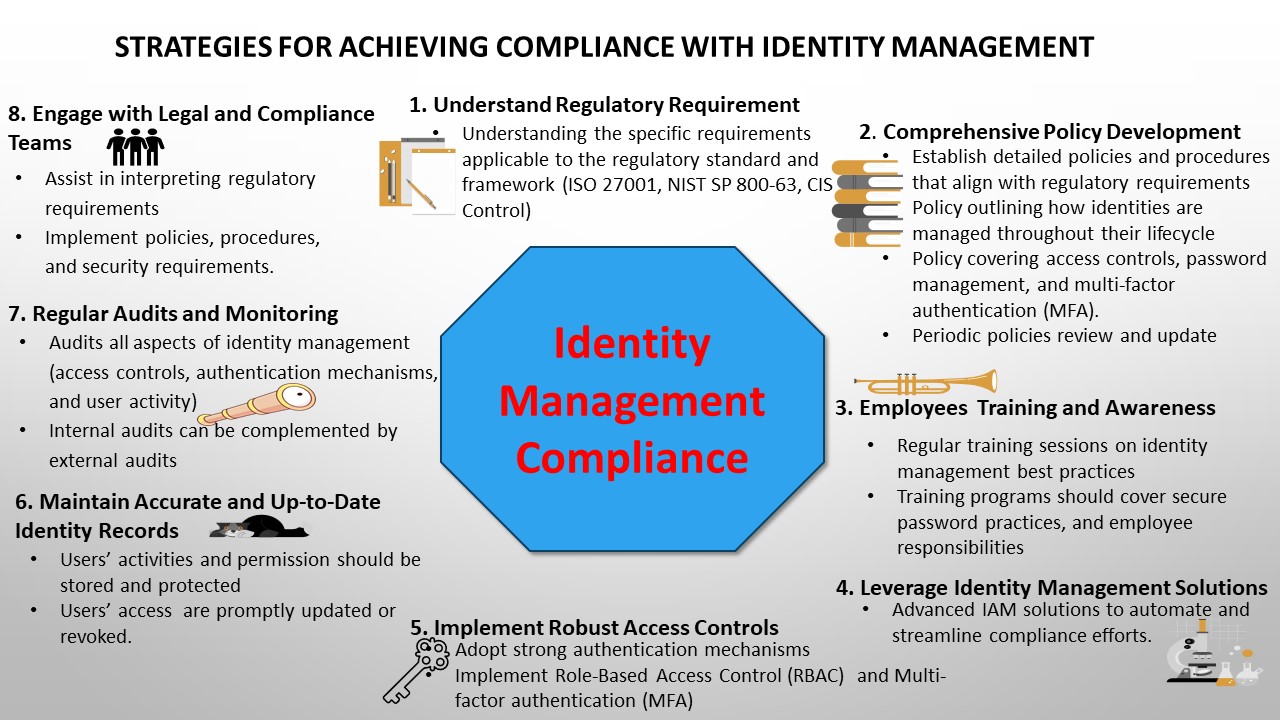
Compliance with identity management regulations ensures that organizations safeguard sensitive data, maintain user privacy, and adhere to legal standards. Here are eight key strategies to help achieve and maintain compliance with identity management regulations:
- Understand Regulatory Requirements:
The first step towards compliance is understanding the specific requirements applicable to the regulatory standard and framework. Common requirements include:
- ISO/IEC 27001: Provides a comprehensive approach to information security management, including identity and access management (IAM).
- NIST Special Publication 800-63: Offers guidelines on digital identity services, including authentication and lifecycle management.
- CIS Controls: Provides a set of best practices for securing IT systems and data, including IAM controls.
- Comprehensive Policy Development:
Organizations need to establish detailed policies and procedures that align with regulatory requirements. The set of policies for identity management must outline how identities are managed throughout their lifecycle, from creation to deactivation. Also, the policies should cover areas like access controls, password management, and multi-factor authentication (MFA). Additionally, organizations should establish a schedule for periodic reviews and updates of the documented policy based on changes in regulations and best practices. Regularly reviewing and updating identity management policies ensures ongoing compliance.
- Employees Training and Awareness:
Employees play a critical role in maintaining compliance. Thus, regular training sessions for employees on identity management best practices and regulatory requirements are essential. Training programs should cover topics such as secure password practices, and their role in ensuring compliance in the organization.
- Leverage Identity Management Solutions:
Leverage advanced identity and access management solutions to automate and streamline compliance efforts. These solutions can provide centralized management of user identities and access permissions, automated provisioning and de-provisioning of user accounts, and comprehensive reporting and audit trails for compliance verification.
- Implement Robust Access Controls:
Access control mechanisms are critical for safeguarding sensitive data and critical assets. Adopt strong authentication mechanisms to verify user identities. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to ensure users have appropriate access based on their roles and job functions within the organization. Also, ensure multi-factor authentication (MFA) is implemented across systems.
- Maintain Accurate and Up-to-Date Identity Records:
Regulations often mandate that organizations maintain accurate records of users’ activities. Users’ activities and permission should be stored and protected from unauthorized access. Use automated systems to manage user access rights, ensuring that when an employee’s role changes or they leave the organization, their access is promptly updated or revoked.
- Regular Audits and Monitoring:
Regular audits help identify non-compliance issues and areas for improvement. Internal audits should be complemented by external audits to provide an unbiased assessment of compliance. Audits should cover all aspects of identity management, including access controls, authentication mechanisms, and user activity monitoring.
- Engage with Legal and Compliance Teams:
Consulting with legal and compliance teams can provide valuable insights and ensure that the organization’s identity management practices are in line with regulatory requirements. Compliance experts can also assist in interpreting regulatory requirements, implementing necessary changes to policies and procedures, and implementing appropriate requirements.
Conclusion
Achieving compliance with identity management regulations is a multifaceted challenge that requires a strategic approach. By understanding regulatory requirements, implementing robust security measures, conducting regular audits, and fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can ensure regulatory compliance and effectively manage identity-related risks. These strategies not only help avoid legal repercussions but also enhance overall security and trust in the organization’s identity management practices.